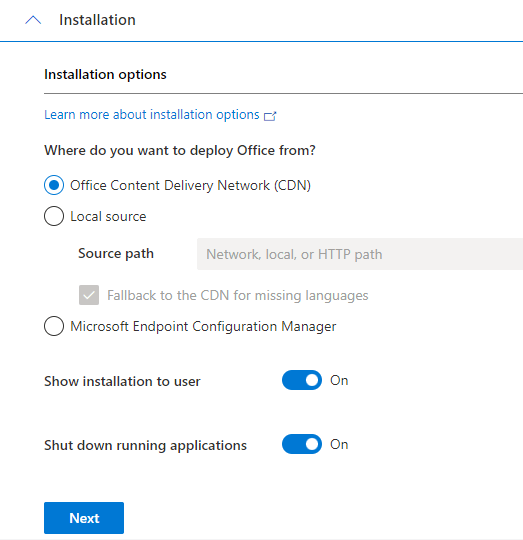
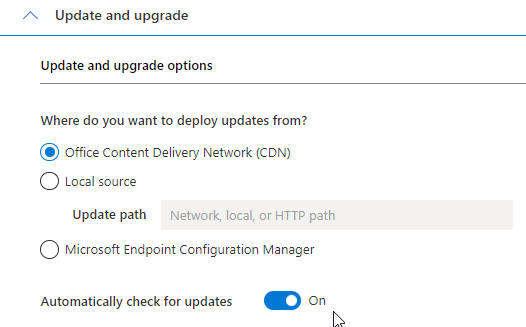
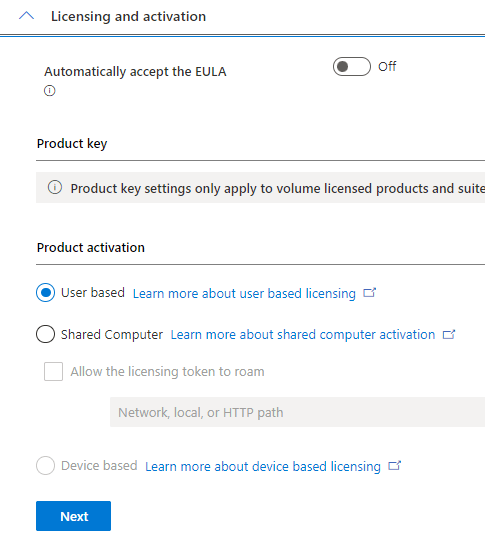
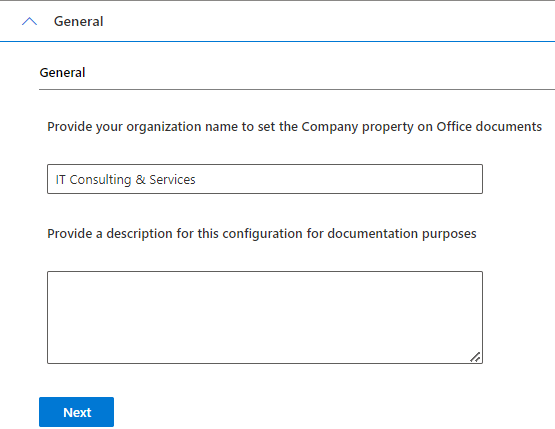
How AWS is Transforming the Pharmaceutical Sector in Pakistan
The pharmaceutical industry in Pakistan has been steadily growing over the years and is now one of the largest revenue-generating sectors in the country. With the increasing demand for quality healthcare products and services, the need for advanced technologies to support the pharmaceutical industry has also become crucial. This is where cloud computing, particularly Amazon Web Services (AWS), comes into play.
AWS is a cloud computing platform that offers a wide range of services and tools to help businesses of all sizes and industries manage their data, applications, and operations efficiently. For Pakistani businesses in the pharmaceutical sector, utilizing AWS can bring about numerous benefits and help them stay competitive in the ever-evolving healthcare landscape.

One of the main advantages of using AWS for pharmaceutical businesses is cost reduction. Traditional on-premise data centers and IT infrastructure require a significant amount of investment and maintenance costs. With AWS, businesses can reduce their hardware and IT expenses, as they do not need to invest in physical servers, storage, or networking equipment. AWS also offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, allowing businesses to only pay for the resources they use, making it a cost-effective solution for pharmaceutical companies of all sizes.
Another key benefit of AWS is scalability. The pharmaceutical industry is highly volatile, and the demand for drugs and medical products can fluctuate drastically. With AWS, businesses can easily scale their resources up or down, depending on the demand, without any disruption in operations. This also means that businesses can quickly adapt to market changes and launch new products or services without worrying about IT limitations or infrastructure costs.
Data security is a significant concern in the pharmaceutical industry, where sensitive patient data and confidential research and development information are constantly being handled. AWS offers advanced security features, including encryption, access control, and compliance certifications, to ensure that businesses’ data and operations are protected from potential cyber threats. With AWS, businesses can have peace of mind knowing that their data is secure and compliant with industry regulations.
The pharmaceutical industry in Pakistan also heavily relies on data analysis and research to develop new drugs and improve existing products. AWS provides a range of data analytics and machine learning tools that can help businesses gain valuable insights from large and complex datasets. This can aid in identifying market trends, predicting demand, and optimizing business processes to make data-driven decisions.
Additionally, AWS also offers various communication and collaboration tools, such as Amazon Chime and Amazon WorkSpaces, that can help pharmaceutical businesses improve their internal communication and collaboration processes. This is especially beneficial in the current remote work environment, where teams need to work together efficiently to meet business goals.
In conclusion, the benefits of using AWS for Pakistani businesses in the pharmaceutical sector are numerous. It can help businesses reduce costs, improve scalability, enhance data security, and gain valuable insights from data analytics. With the support of AWS, pharmaceutical businesses in Pakistan can streamline their operations, stay competitive, and continue to grow in the dynamic healthcare industry.